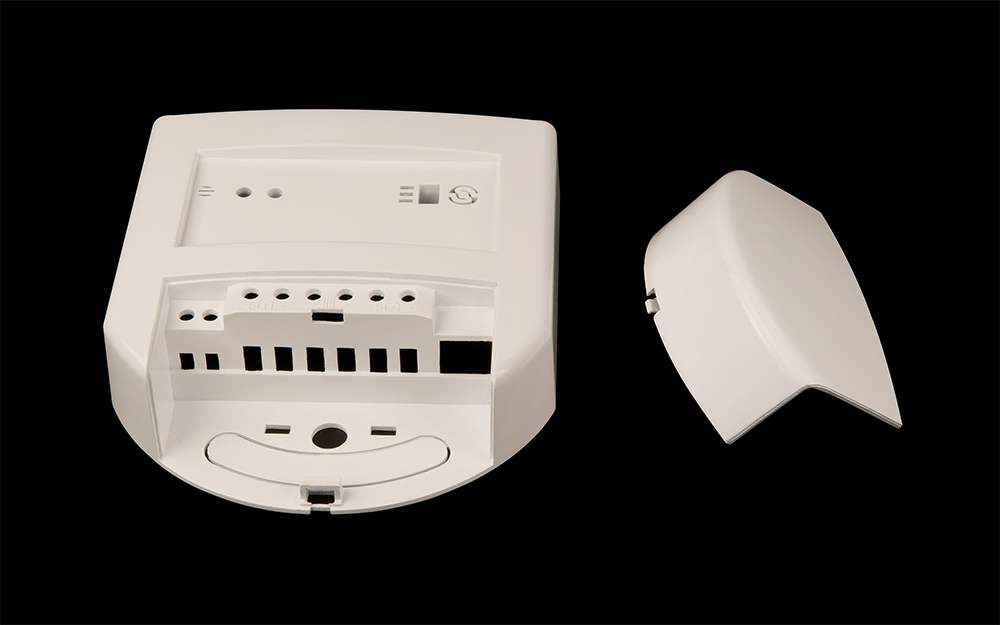
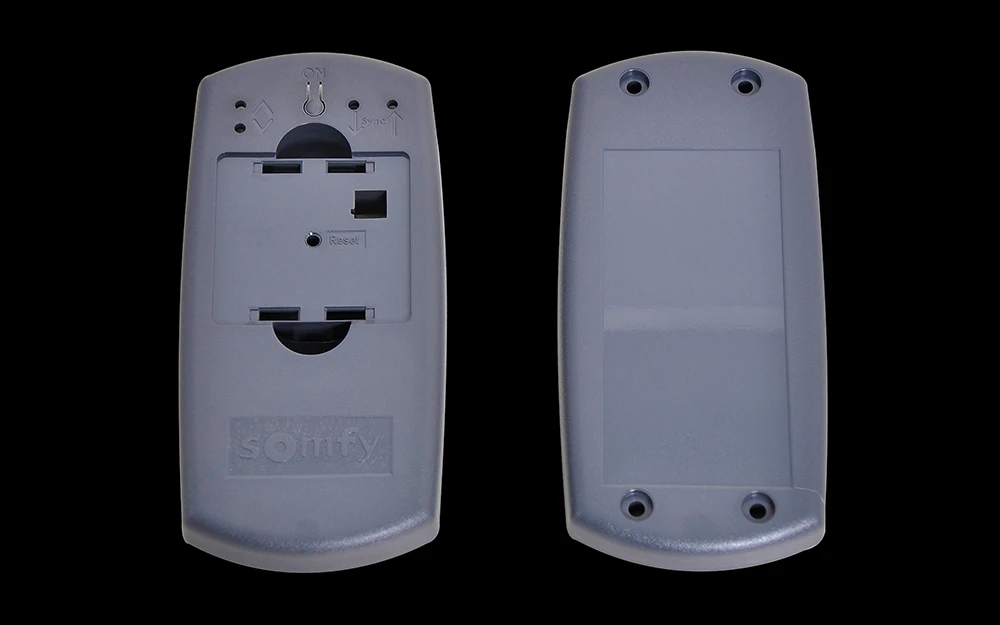
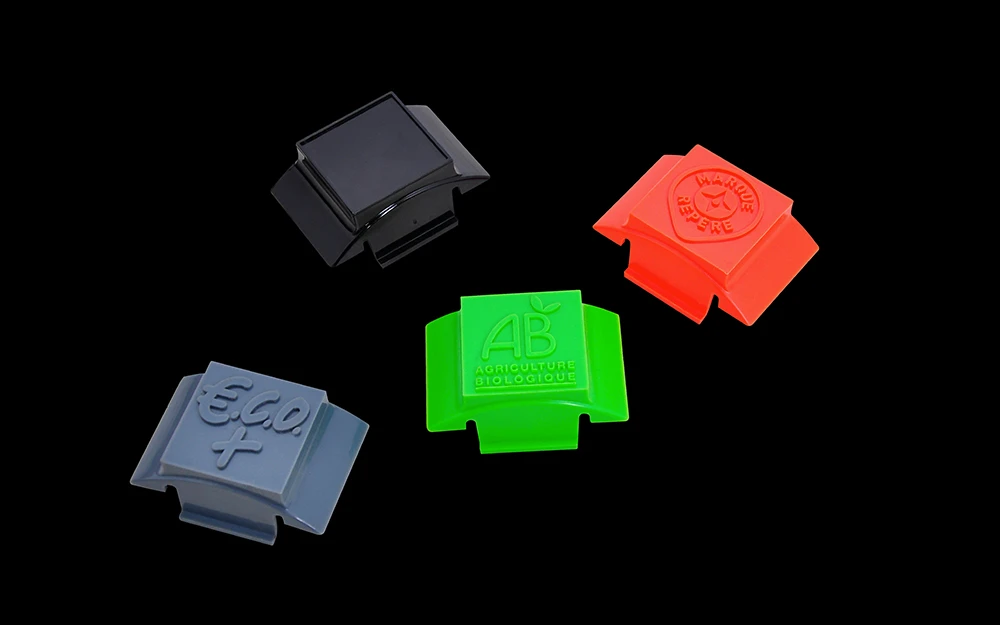
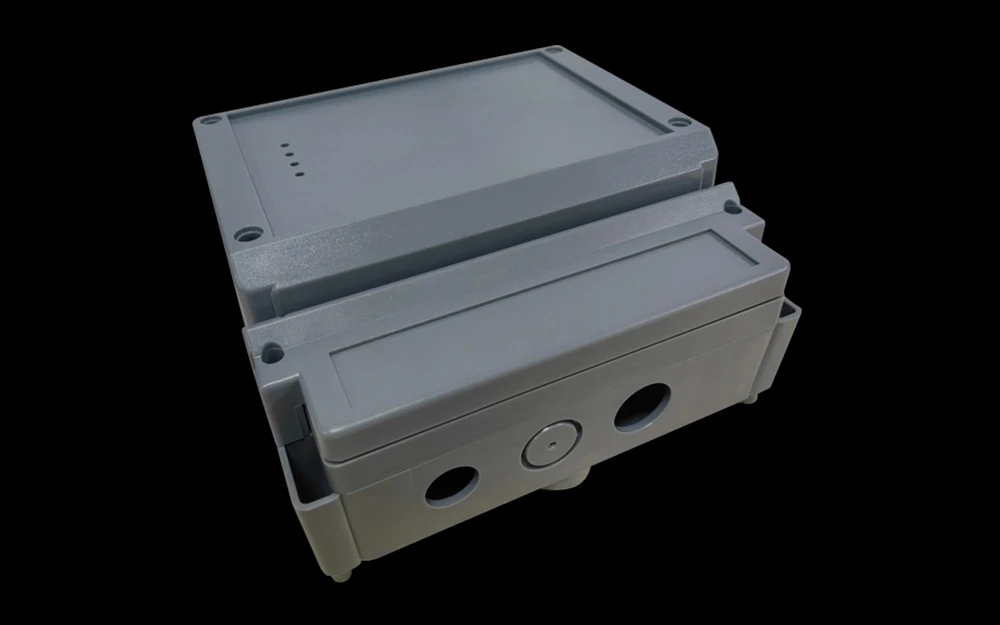
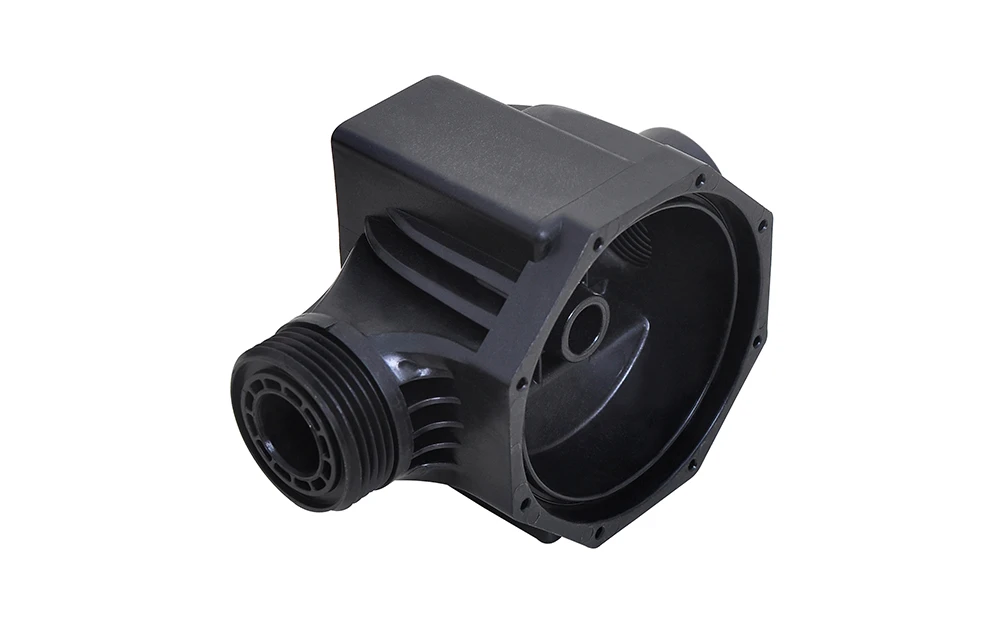
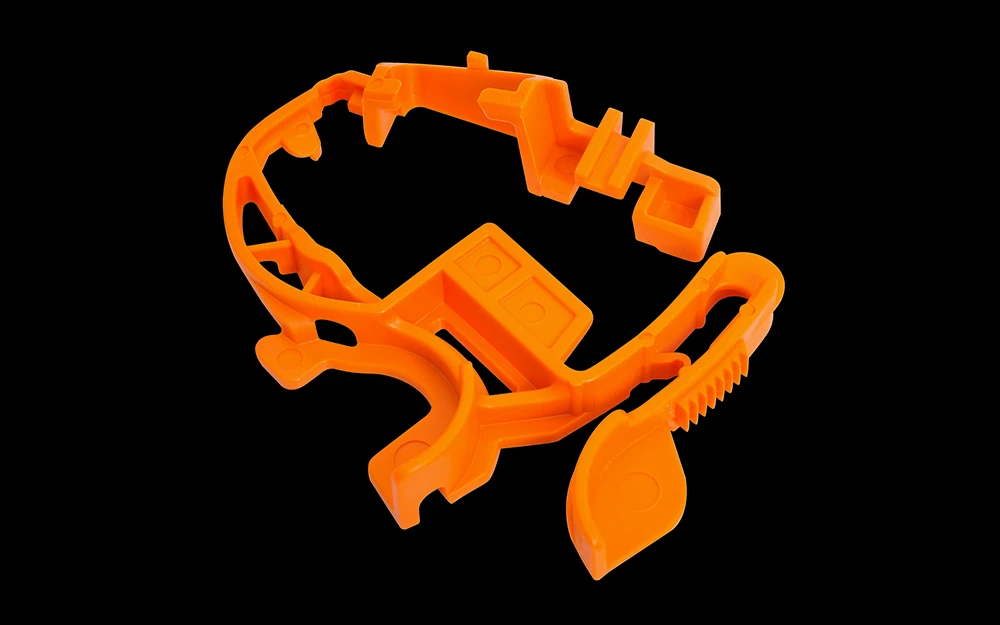
Rapid Plastic Injection Molding Services
Our rapid injection molding service is designed to support your prototyping and low-volume production needs by delivering custom, cost-effective plastic parts quickly. By using optimized prototype tooling, we accelerate development cycles and significantly reduce overall manufacturing costs.
- Quotation in 24 hours
- 1 to 1000+ parts
- Ready within 3+ weeks
- Best for precise plastic prototyping
- Low rapid tooling cost
What is rapid injection molding?
At Protolis, our prototype molding service delivers custom plastic parts fast—ideal for prototype injection molding and low-volume production. With quick-turn tooling and expert DFM support, we help accelerate your development cycle and move from prototype to production in 2 to 4 weeks.
Using the same high-pressure injection molding process as mass production, Protolis ensures consistent quality, tight tolerances, and production-grade finishes. We offer a wide selection of engineering plastics, including ABS, PC, PP, PA, and flame-retardant, UV-stabilized, and custom-colored materials.
This makes our rapid injection molding solution perfect for automotive, medical, consumer electronics, and industrial applications needing fast, reliable molded components.
What is rapid injection molding?
Helping you acheive your prototype
Our rapid injection molding service supports a wide range of part sizes and complexities, making it ideal for producing functional prototypes, housings, connectors, brackets, and other precision plastic components for testing, validation, and market launch.

Overmolding and insert molding
Our expertise enables to create a single part composed of multiple materials and integrated parts with metal inserts.

Rapid tooling
With our cost-efficient rapid prototype tooling, we enable our clients to benefit from shorter production times and parts with fewer geometric constraints.

Post-processing
Our finishes and fitting techniques ensure the final appearance, functionality, and quality of the final assembled parts.
Injection molding capabilities
At Protolis, our in-house mold workshop allows us to produce bespoke rapid tooling with fast a short lead time for rapid injection molding and low-volume production. With more than 20 injection molding machines—ranging from 70t to 1200t—we can manufacture custom plastic parts of all sizes, from small technical pieces to large, complex components. Most post-processing and finishing steps are completed internally, ensuring consistent quality and quick turnaround. By combining custom mold making, rapid tooling, and dedicated processes for small-scale injection molding, Protolis delivers full industrial capability optimized for prototypes, bridge production, and short-run manufacturing.
Your project in 6 steps
Get your plastic prototypes or small-scale production injected parts in no time. A flexible organization providing a personalized response to your need without any setback.
Your quote
Upload files and specifications
DFM
Design optimizations
Rapid tooling
Sampling and adjustments
Production
Close follow-up
Quality control
Dimensional report, pictures, and videos
Delivery
Packing, door-to-door tracking
Applications
Plastic injection molded parts find extensive applications across diverse industries, including automotive, electronic, medical, packaging, and more. This manufacturing process is suitable for creating a variety of parts, including casing, housings, containers, medical equipment, consumer appliances, and many more.
Proven Expertise in Plastic Injection Molding
Protolis provides plastic injection molding service for prototypes and low-volume production, serving medical, industrial, and electronic applications. Our Case Studies demonstrate how we translate design intent into reliable molded parts—covering tooling strategy, DFM optimization, material selection, surface finishing, and controlled lead times.
Explore these real-world projects to gain practical insights and proven best practices for your own plastic injection molding program.
Proven Expertise in Plastic Injection Molding

Plastics for Injection Molding
We provide an extensive selection of production-grade thermoplastics for prototype injection molding and on-demand manufacturing. Selecting the right plastic is crucial to achieving functional, reliable prototypes, and our engineers can help you choose the ideal material. Below is a non-exhaustive list of commonly used materials for plastic injection molding.
Rapid molding finishes
With dedicated finishing facilities and proven expertise, Protolis delivers a broad selection of finishes that elevate the look, performance, and durability of your plastic molded components.

The pigmentation process makes it possible to produce pieces naturally colored in the mass of certain plastics. It is possible to choose the desired RAL or Pantone, with color pigments mixed with the material. This is applicable for rigid or flexible parts.

This type of finishing is a high-level polishing, also known as mirror polishing, that gives the part a smooth, reflective, and aesthetically pleasing appearance.

There are several degrees of transparency depending on the technologies and materials used. The opacity can also be manually adjusted by polishing, sanding, or pigmentation.

Chrome plating is a technique of applying a thin layer of chromium onto a substrate through galvanic or vacuum plating. This additional layer not only improves the aesthetic but prevents corrosion and wear.

Whether by applying a surface treatment or by pigmentation, matching the colors of your prototypes and parts is important for meeting your specifications and the visual quality of the final product.

We offer various methods to print or engrave your logo, texts, and symbols to give a finished appearance to your pieces.
General rapid injection characteristics
Why Choose Protolis for Prototype Molding Service?
- Fast lead times — first molded parts as fast as 2–4 weeks
- 24-hour quotation with DFM support
- In-house mold workshop with 20+ machines
- Optimized for prototypes and low-volume production
- Wide range of engineering plastics
- Consistent quality control aligned with ISO 9001 standards
Why Choose Protolis for Prototype Molding Service?
Rapid injection molding FAQs
What are the common defects in plastic injection molding and how can they be prevented?
Injection molding is a complex technology with various potential defects, each requiring careful consideration for prevention:
- Warping can occur due to uneven cooling, emphasizing the importance of a well-designed cooling system and precise control of process parameters.
- Sink marks, small depressions on the surface, can be minimized by maintaining uniform wall thickness and optimizing pressure and time settings.
- Short shots, incomplete parts, can be prevented by ensuring the material is at the correct temperature and the mold is adequately vented.
- Flash, excess material escaping the mold, is mitigated through proper maintenance, clamping force, and material viscosity control.
- Burn marks, discoloration on the part, are prevented by optimizing gas venting, controlling melt and mold temperature, and adjusting injection speed.
Our guidelines provide further insight into managing these complexities.
What material is used for prototype molds?
When considering materials for prototype molds, aluminum stands out as the most common choice, often interchangeably referred to as an “aluminum mold” synonymous with prototype or pilot molds.
The appeal of aluminum lies in its exceptional heat conductivity, facilitating quicker cooling and more efficient machining. However, the popularity of aluminum has diminished due to its limitations in terms of strength and durability. To address these concerns, we advice for the use of steel with a hardness of 30 HRC. Advances in machining technology, particularly with high-speed CNC, have significantly improved the machinability of steel, reducing the historical gap that favored aluminum. This shift positions steel molds with 30 HRC as a compelling alternative for prototype applications.
How cost-effective is plastic injection molding for rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing?
Unfortunately, it is not the most cost-effective method for these purposes due to high setup fees (injection tooling), limited design flexibility, and longer lead times. However, it remains a unique technology capable of delivering high-quality parts with impeccable finish and dimensions. The extensive range of available grades, each with specific properties, is immensely advantageous compared to other prototyping technologies. To enhance cost-effectiveness, the key lies in minimizing the initial investment in molds, especially through the use of prototype molds. We have developed a specialized knowledge and methodology to achieve this goal.
Related resources
Plastic Injection Molding Guide
Thermoplastics for medical devices: materials, technologies, and best practices