3D printing
At Protolis, we provide high-quality 3D printed plastic and metal parts to provide quick solutions for complex prototypes and production. Our 3D printing services are:
- Suitable for highly complex parts
- Available in 20+ production grades of plastic and metal materials
- Ready within 3-5 business days
- Enhanced with the most advanced additive production technologies available
- Available with 10+ finishing options
What is 3D printing?
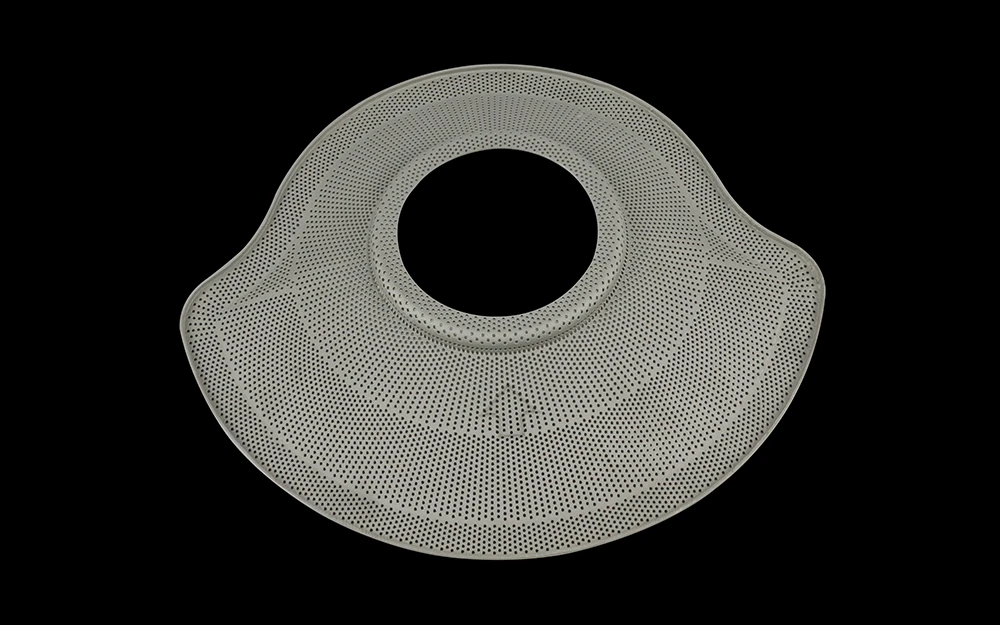
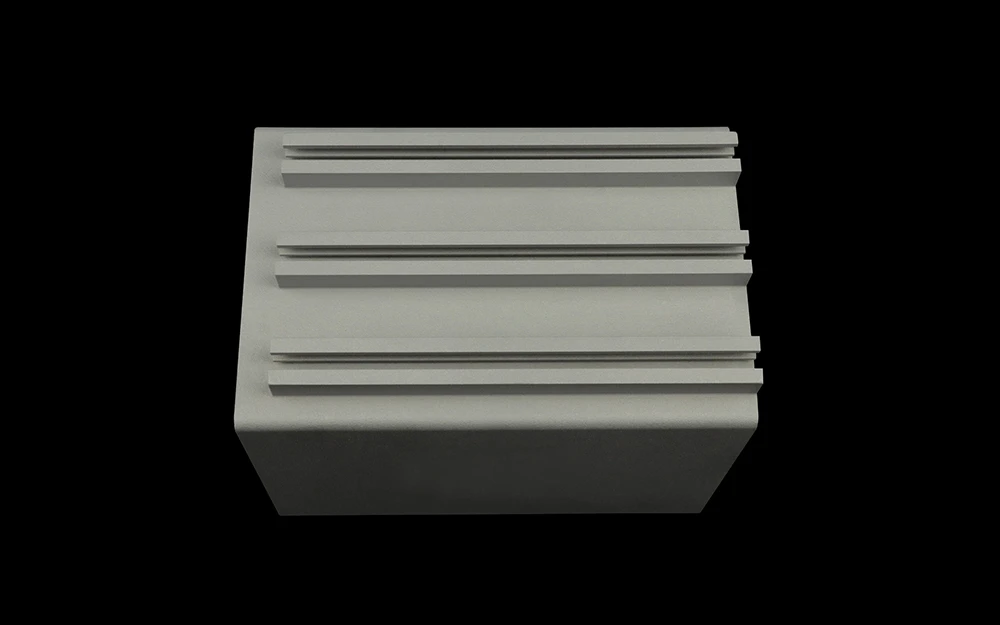
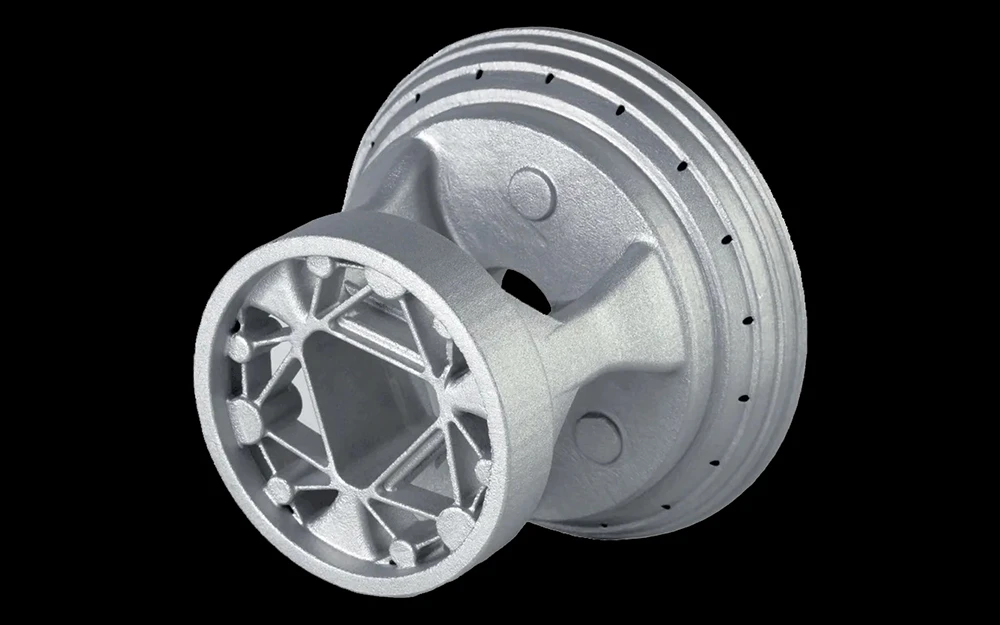
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer based on a digital model. It is used to produce complex metal and plastic parts, including hollow bodies and parts with undercuts, rapidly and with a high level of precision, which traditional machining technologies may not be able to achieve.
What is 3D printing?

3D printing processes
Our 3D printing capabilities meet a wide variety of manufacturing needs, producing both simple and complex shapes for prototyping and low-volume production of high-quality parts.

Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA is the oldest, most affordable, and most frequently used method in 3D rapid prototyping technology. This production method allows the quick creation of models or plastic parts with high precision, large dimensions, and complex geometries.

Selective laser sintering (SLS)
SLS is an additive manufacturing technology typically used for plastics or metals, using a laser to fuse powdered materials and create complex 3D objects without support structures. It is a precise and affordable solution for low-volume production in various industries.

Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS)
DMLS is a top 3D printing method for metal parts, utilizing successive layers to selectively fuse metal powder with a laser, resulting in superior mechanical properties and high precision in the production of high-quality metal components.
Your project in 5 steps
Get your plastic and metal prototypes or production parts in no time. A flexible organization providing a personalized response to your need without any setback.
Your quote
Upload files and specifications
DFM
Design optimizations
Production
Close follow-up
Quality control
Dimensional report, pictures, and videos
Delivery
Packing, door-to-door tracking
Applications
Due to its low cost and rapid production capabilities, 3D printing is commonly used for various applications such as creating concept models, visual aids, functional prototypes, and more. 3D printing is utilized in various industries such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, architecture, fashion, and consumer products.
Additionally, thanks to its versatility, it enables the production of complex parts that may not be achievable with other manufacturing technologies.
3D printing materials
We offer access to a wide range of production-grade plastic and power metal materials for your prototype and low-volume production parts. Below is a non-exhaustive list of commonly used materials for 3D printing:
General 3D printing characteristics
3D printing finishes
There are numerous finishing options available in 3D printing. These finishing processes can improve the appearance, functionality, and durability of the part. They involve either machine or hand processing.

A paint finish that enhances the surface condition both functionally and aesthetically. It is possible to achieve different effects of appearance: satin, matte, gloss, or semi-gloss.

Powder coating is similar to liquid spray paint, except that this process uses a dry powder. It improves the resistance to wear and corrosion. The resulting surface is uniform.

This polishing generally involves changing the level of roughness of a surface by various manual, mechanical, or chemical techniques. This can change the dimensional or geometric accuracy of the part.

This type of finishing is a high-level polishing, also known as mirror polishing, that gives the part a smooth, reflective, and aesthetically pleasing appearance.

There are several degrees of transparency depending on the technologies and materials used. The opacity can also be manually adjusted by polishing, sanding, or pigmentation.

Brushing is a surface finishing method that forms continuous paralleled lines on the surface of metal parts. The purpose is usually to obtain a decorative effect with a slight level of reflection.
3D printing capabilities
At Protolis, we partner with a large network of certified 3D printing shops to ensure access to the latest additive manufacturing technology. You will work with experts to find the right fit for your project from a wide range of 3D printing processes. Once the parts are printed, we provide in-house post-processing operations such as threading, polishing, and precise CNC machining.
3D printing FAQs
What are the benefits of 3D printing?
When considering the advantages of 3D printing, two key benefits stand out: speed and design freedom. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing offers rapid prototyping and production capabilities, allowing for quicker turnaround times and accelerated product development cycles. Additionally, 3D printing provides unparalleled design freedom, enabling the creation of complex geometries and intricate structures that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using an other manufacturing technique.
What materials are best to use with 3D printing?
The choice of materials for 3D printing depends on the intended application, cost considerations, and more. However, some commonly used materials include:
- For Plastic: ABS (easy to process and cost-effective) and PLA (user-friendly with a good finish).
- For Metal: Stainless steel (offering a good balance of quality and price, corrosion-resistance, and relative strength without the high cost associated with titanium).
How long does a prototype take with 3D printing?
The time it takes to create a prototype with 3D printing can vary significantly, from around 30 minutes to several hours. The primary factors influencing the duration are the size of the prototype, the material used, and the type of 3D printing. 3D printing is usually one of the quickest technologies in comparison to others.
Related resources

Extrusion Guide

Racing car bodywork for one of the world’s premier auto shows