Metal materials for 3D printing
Metals offer versatile solutions in 3D printing, particularly for small series and prototyping projects. Protolis provides a wide range of metal grades, each tailored to offer distinct advantages.
- Availability: Metal 3D printing materials come in various types, allowing for a wide range of applications. Gain access to the right material for your specific 3D printing needs.
- Customization: Choose from a diverse range of finishes for both aesthetic and functional possibilities.
Common 3D metals
Discover the possibilities of metal materials for 3D printing.
Description
Modified ultra-low carbon Cr-Ni-Mo series austenitic stainless steel with good mechanical properties, high hardness, strength & ductility, superior acid & corrosion resistance, suitable for marine environments.
Applications
Medical technologies
Automotive industry
Aerospace engineering
Marine components
Description
This grade is lightweight and has good mechanical properties, including high strength and dynamic load capacity as well as good thermal and electrical conductivity with high corrosion resistance. Properties can be modified with heat treatments.
Applications
Engineering components subject to high loads
Lightweight designs
Aerospace and automotive components
Description
This class of metal superalloy is characterized by excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and temperature resistance.
Applications
Automotive
Aerospace
Biomedical
Description
A steel grade with good mechanical properties, including high strength, toughness, and wear resistance. It can be easily post-hardened to more than 50 HRC properties, adjustable with different heat treatment. It also shows good machinability and excellent polishability.
Applications
Mold inserts, tools, and equipment
High-performance industrial and engineering parts (aerospace, motorsports)
Description
This alloy is a nickel-chromium superalloy. It is well known for its high strength, outstanding corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It can be heat treated and material properties can be varied.
Applications
Aerospace
Nuclear and chemical process equipment
Description
A low-density, alpha-beta titanium alloy widely used for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance.
Applications
Aerospace
Shipbuilding
Automotive
Medical
3D metal printing services
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, creates precise, complex metal parts—including hollow and undercut components—using layer-by-layer material addition from digital models to surpass traditional machining in speed and precision.
At Protolis, we offer metal 3D printing services for low-volume manufacturing and rapid prototyping. We provide high-quality 3D production processes including direct metal laser sintering (DMLS).
3D metal printing services
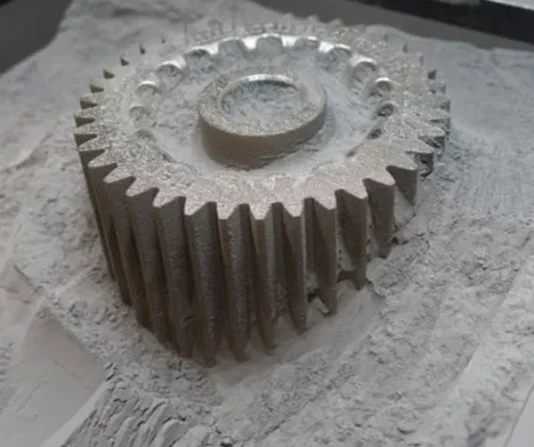

Our finishes for metal 3D printing
Our selection of 3D printed metal parts comes with a variety of finishing options, such as powder coating, polishing, brushing, and sandblasting. Select your preferred finishing option for enhanced functionality and aesthetics.

Powder coating is similar to liquid spray paint, except that this process uses a dry powder. It improves the resistance to wear and corrosion. The resulting surface is uniform.

This polishing generally involves changing the level of roughness of a surface by various manual, mechanical, or chemical techniques. This can change the dimensional or geometric accuracy of the part.

This type of finishing is a high-level polishing, also known as mirror polishing, that gives the part a smooth, reflective, and aesthetically pleasing appearance.

Brushing is a surface finishing method that forms continuous paralleled lines on the surface of metal parts. The purpose is usually to obtain a decorative effect with a slight level of reflection.

A paint finish that enhances the surface condition both functionally and aesthetically. It is possible to achieve different effects of appearance: satin, matte, gloss, or semi-gloss.

Sand blasting is the high-pressure projection of silica sand on the surface of the workpiece to create a matte surface, including creating aesthetic consistency for plastic and metallic parts.
To learn more about these finishing options, please refer to our finishes page here.
Our 3D metal printing characteristics
Your project in 5 steps
Get your 3D metal prototypes in no time with Protolis. Here’s how our efficient, flexible process typically works.
Your quote
Upload files and specifications
DFM
Design optimization
Production
Close follow-up
Quality control
Dimensional report, pictures, and videos
Delivery
Packing, door-to-door tracking
3D printing metals FAQs
What is the main technique used in 3D printing metal?
Metal powder bed fusion is a widely used technique in metal 3D printing, with direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) being a prevalent method. In DMLS, a high-powered laser is employed to melt and fuse metal powders together. This process is known for its proficiency in creating precise metal components with intricate details and complex shapes, surpassing conventional methods. Moreover, its additive nature minimizes material waste, offering cost-effective and environmentally conscious manufacturing.
Which metals are best for 3D printing?
Titanium is one of the best metals for 3D printing, boasting a remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. It finds extensive applications in aerospace, medical implants, and the automotive industry. However, it’s worth noting that it comes with a higher cost. For a more common and cost-effective option with a good balance of strength and ductility, stainless steel is widely used in 3D printing. Varieties like 316L and 17-4 PH offer corrosion and oxidation resistance, making them suitable for industrial, medical, and consumer goods applications.
Are metal 3D printing strong?
The strength of 3D printed metal parts can be comparable to those manufactured by traditional methods, but it varies based on the material and printing process.
Related resources

Extrusion Guide

Racing car bodywork for one of the world’s premier auto shows