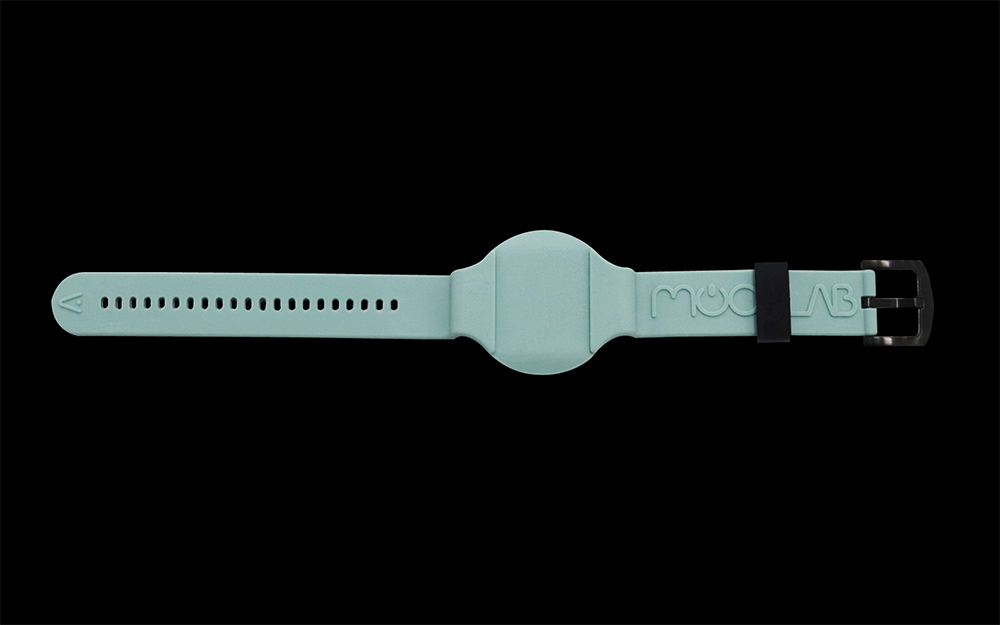
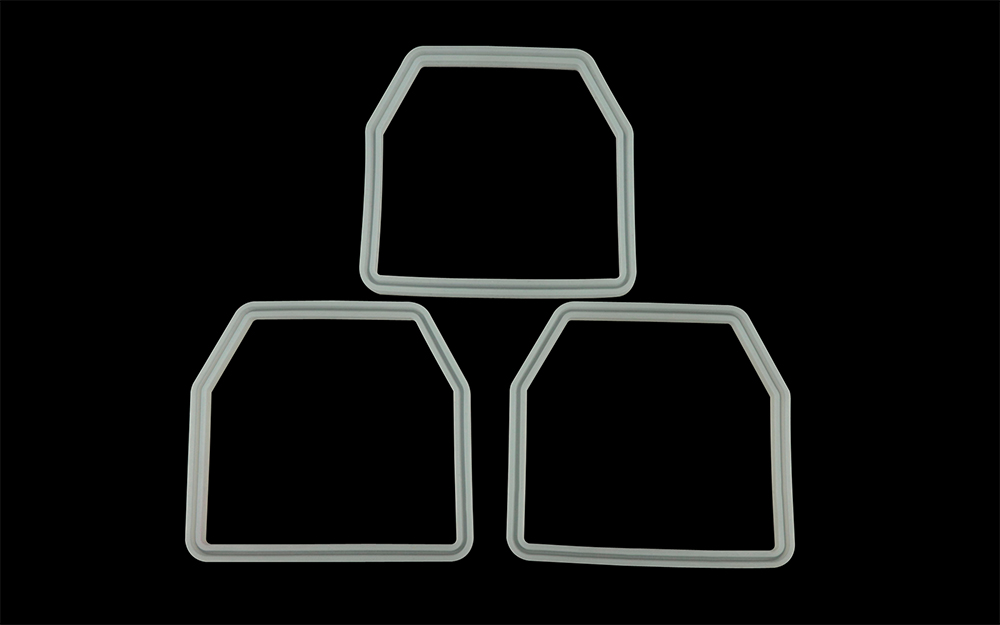
Rubber and silicone for compression molding
Rubber and silicone used for compression molding are flexible and resilient materials that are molded under pressure and heat to create a wide range of products. Protolis provides a selection of production-grade options for prototyping and on-demand manufacturing, including:
- Seven production grades ready for molding.
- Specific grades and shore on demand: Access the right material for your specific compression parts needs.
- Customization: Choose from a diverse range of colors and finishes for both aesthetic and functional possibilities.
Common compression molding materials
Discover the possibilities of elastomers for compression molding.
Description
Vinyl methyl silicone (VMQ) is well known for its wide temperature range and excellent elongation at break.
Applications
Food and medical
Description
This is a synthetic rubber compound with unique resistance to oil, fuel, and chemicals. It’s the most-used rubber with good mechanical properties.
Applications
Sealing application in many industries.
Description
Non-synthetic NR is extracted from the Hevea tree, with polyisoprene (IR) bring the synthetic equivalent. They both have high tensile strength, good abrasion resistance, and are extremely waterproof.
Applications
Anti-vibration mounts
Drive couplings
Tires
Springs
Bearings
Rubber bands
Description
EPDM offers excellent resistance to heat, water and steam, alkali, mild acidic and oxygenated solvents, ozone, and sunlight (UV).
Applications
Construction
Automotive
Electric devices
Description
Polyurethane elastomer has excellent wear and tear resistance, high tensile strength, and high elasticity.
Applications
Hydraulic and reciprocating seals, gaskets, diaphragms, hoses, and conveyor belts.
Description
This grade replaces natural rubber (more economically friendly) with excellent abrasion resistance and crack endurance, and generally ages well. It has good compression set resistance and water resistance.
Applications
Car tires
Shoe soles and heels
Drive couplings
Automotive parts
Mechanical rubber goods
Description
This is a high-value rubber that provides extraordinary levels of resistance to chemicals, oil, high temperatures, and UV.
Applications
Seals, o-rings, and hoses for a variety of high-performance applications
Rubber compression molding services
Compression molding is a process where a heated polymer is placed into a mold cavity and compressed into the desired shape. This production method uses hydraulic presses with heated platens to achieve the desired forming temperature.
At Protolis, we have a team of skilled professionals who specialize in compression molding and offer their expertise to meet your specific manufacturing needs.
Rubber compression molding services

Our finishes for compression molding
Our range of compression molded flexible elastomer parts comes with a variety of finishing options, such as technical or cosmetic polishing.

The pigmentation process makes it possible to produce pieces naturally colored in the mass of certain plastics. It is possible to choose the desired RAL or Pantone, with color pigments mixed with the material. This is applicable for rigid or flexible parts.

Whether by applying a surface treatment or by pigmentation, matching the colors of your prototypes and parts is important for meeting your specifications and the visual quality of the final product.

We offer various methods to print or engrave your logo, texts, and symbols to give a finished appearance to your pieces.
To learn more about these finishing options, please refer to our finishing page here.
Our compression molded rubber characteristics
Your project in 6 steps
Get your rubber and silicone compression molding parts in no time with a flexible organization that always provides personal responses without any setbacks.
Your quote
Upload files and specifications
DFM
Design optimization
Tooling
Mold production and first samples for approval
Production
Close follow-up
Quality control
Dimensional report, pictures, and videos
Delivery
Packing, door-to-door tracking
Compression molding FAQs
What are the differences between silicone and natural rubber in compression molding?
First, natural rubber is a derived from the latex of the rubber tree and is known for its elasticity, tear resistance, and abrasion resistance, whereas silicone is a synthetic material made from silicon, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. Natural rubber is biodegradable and cost-effective for many applications, but also poses allergenic potential, is sensitive to heat and UV exposure, and has limited chemical resistance. Silicone doesn’t have these limitations is well knows for its versatility, durability, and ease of maintenance and cleaning. These advantages make silicone a preferred material for baby products as well as kitchen and medical applications.
Can you achieve complex geometries with rubber compression molding?
Yes, absolutely. Rubber compression molding is a versatile process capable of producing a variety of complex shapes. Notably, the presence of undercuts is possible thanks to the flexibility of the material, allowing demolding by force.
How do I choose the right rubber material?
It always depends on the industry and specific requirements, but in our industry and for most of our clients, we use thermoset polymers such as NBR, VMQ, and EPDM. These are widely employed for electrical components, automotive parts, and household items due to their electrical insulating properties, heat resistance, and cost-effectiveness.
Related resources

Extrusion Guide

Racing car bodywork for one of the world’s premier auto shows